Student: Adrian Curtze-Rodriguez
Supervisor: Christopher Ripp
Time period: 11/19/2018 - 05/15/2019
Type: Project Seminars Bachelor
Durch das europäischen Market Coupling, welches mittlerweile einen fast vollständigen transnationalen Zusammenschluss aller europäischen Strommärkte und Netze bildet, ist es möglich nahezu zwischen allen europäischen Verbundländern Strommengen auszutauschen. Dadurch können nationale Erzeugungs¬kapazitäten optimaler eingesetzt und die Netzstabilität kosteneffizienter realisiert werden. Unterschiedliche nationale Strategien, der Verwendung von regenerativen oder konventionellen Erzeugungstechnologien, führen dabei zu stark inhomogenen CO2 Intensitäten des jeweiligen Strommixes innerhalb Europas. Durch grenzübergreifenden Energietransfer ergeben sich somit unterschiedliche CO2 Bilanzen zwischen den einzelnen Ländern. Ziel dieser Arbeit ist es, auf Basis der grenzübergreifenden Stromübertragung, eine zeitlich abhängige CO2 Bilanzierung zwischen den europäischen Mitgliedsstaaten zu erstellen. So sollen Fragestellungen beantwortet werden, u.a. wieviel absolute Tonnen CO2 erhält Mitgliedland X von seinen Nachbarländern oder reduziert die nationale CO2 Menge des Nachbarlandes Y. Datenbasis dieser Arbeit sollen ENTSO-E Erzeugungsdaten der einzelnen Mitgliedstaaten und deren jeweiligen Energieübertragungsmengen bilden. Die notwendigen nationalen zeitlich abhängigen CO2 Intensitäten sollen mittels verifizierbarer Annahmen zum Wirkungsgrad der eingesetzten nationalen Erzeugungstechnologien abgeschätzt werden. Diese Arbeit stellt eine anspruchsvolle Aufgabe an eigenständige Datenauswertung und recherche sowie den Umgang mit großen Datenmengen dar. Programmierung mit Matlab oder Python ist erforderlich.
Student: Abdenassir El Amin
Supervisor: Edwin Mora
Time period: 10/19/2018 - 03/01/2019
Type: Project Seminars Bachelor
Im Rahmen des Praktikums soll ein Inselnetz mit 2 konventionellen Generatoren, einer Photovoltaik-Anlage und einer Batterie auf unserem OPAL-Echtzeitsimulator implementiert werden. Simulierte Schalter ermöglichen das zu und wegschalten von physischen oder logischen Komponenten. Ziel ist ein HiL-Test einer dezentralen Sekundärregelung für das Inselnetz. (Mindestens ein Raspberry-Pi als Sekundärregler)
Student: Allan Almeida Santos
Supervisor: Christopher Ripp
Time period: 11/01/2018 - 02/28/2019
Type: Project Seminars Bachelor
Energy system design models examine the transition paths of an energy system, like for example Germany’s, from now until 2050 when major decarbonization targets shall be fulfilled. Such tools model the operation and the generation / storage / transmission capacity changes in the power sector, but also w.r.t. heat and traffic. This breadth of topics is necessary to cover the whole energy system in sufficient detail to obtain plausible results. On the other hand, large coverage renders even small models highly complex and the results difficult to understand, even for the expert. In order to bring the transition plans into reality, however, we need to convince non-technical decision makers, such as politicians and/or company managers, to take appropriate actions. When such decisions have important consequences for their careers – as is often the case – these decision makers want to understand themselves what they will be fighting for. The project shall examine different ways how to derive simple, explainable models that convey the same messages as the detailed models, but are more acceptable by decision makers. The work will be in collaboration with Prof. Frank Jäkel from the cognitive science center.
Student: Daniel Kretschmann
Supervisor: Tim Janke
Time period: 01/01/2019 - 06/30/2019
Type: Master Thesis
The importance of continuous intraday markets for trading electricity is steadily increasing, especially in markets with large share of renewable generation. While day-ahead markets are a well researched topic, the literature on intraday trading is scarce. The goal of this thesis is twofold. First, an exploratory analysis of the EPEX contiuous market will be conducted. Building on this, simple forecast models for weighted mean prices and traded volumes should be developed and tested.
Student: Mu Shouran
Supervisor: Edwin Mora
Time period: 10/19/2018 - 03/01/2019
Type: Project Seminars Bachelor
A control system for an islanded micro grid should be designed in LabView. The information for the GUI will be handled by an OPC-UA server. The project will first be implemented on a local computer (random signals) and then be deployed to our OPAL RT simulator.
Student: Mohamed Ghanmi
Supervisor: Jonas Hülsmann
Time period: 04/15/2019 - 10/15/2019
Type: Project Seminars Bachelor
In progress
Student: Allan Almeida Santos
Supervisor: Edwin Mora
Time period: 02/14/2019 - 08/13/2019
Type: Master Thesis
The standard approach used for power grid stabilization is the so-called primary control, a distributed approach that implements a classical proportional control on each power plant of the network. Although this static control is simple, the parametrization of each node controller is challenging due to the, in practice, lack of knowledge of grid parameters. In addition, addressing analytically the stability of power grids is difficult due to the inherent high coupled nonlinear dynamics and the large amount of unknown network parameters. Reinforcement Learning techniques have the potential for solving control problems, for which high environment uncertainties can/must be assumed. For this work, each power plant is/could be equipped with a local agent. Local agents have to interact with each other for finding plausible local control actions. Moreover, two study cases have to be considered: action with policy constraints (adaptation of static standard primary control parameters) and action without policy constraints. Thus, this work has to associate tools from reinforcement learning and control theory for solving the problem of automatic grid frequency stabilization.
Student: Alvaro da Rocha Albertini
Supervisor: Johannes Börner
Time period: 03/04/2019 - 09/04/2019
Type: Master Thesis
Classical N-1 considers the random outage of any component in the power system. It guarantees that the system still runs smoothly in that case. What we call modern N-1 should also consider the intended misbehavior of any component. This is of ever greater importance as system become more and more digitalized and cyber attacks more common and professional. Of special importance for the power system ar HVDC lines due to their large capacity and their ability for fast and well-controllable dynamics. The thesis should examine the different effects that a successful hacker of the controller of an HVDC line could produce. The thesis should work on a qualitative level and survey potential attack directions. It should also simulate the effects in a high time-resolution simulation of an exemplary two zone power system connected via an HVDC link. Of interest are both short term distortions such as (partial) blackouts but also the destruction of the underlying hardware, as this would have long term dangerous consequences. The thesis should conclude with first indications how the most detrimental effects could be avoided.
Student: Thomas Marion
Supervisor: Johannes Börner
Time period: 09/10/2018 - 03/11/2019
Type: Master Thesis
Im Bereich der Rechenzentren ist die Virtualisierung von Rechnern und Netzwerken bereits weit fortgeschritten. Mit dieser Arbeit soll die Virtualisierung von Regelnetzen (Virtual Control Function, VCF) mit Anwendung im Energiebereich für Software Defined Networking (SDN) optimiert werden. Besonderes Augenmerk soll dabei auf der optimalen Einbettung der VCF im SDN unter Berücksichtigung der Qualität der Regelung bei Änderungen der Einbettung gelegt werden.
Student: Andreas Bott
Supervisor: Tim Janke
Time period: 04/01/2019 - 09/30/2019
Type: Master Thesis
Short and medium term prediction of electricity wholesale prices is usually done by either employing statistical time series models or fundamental merit order type models. Lately, Ziel & Steinert (2017) proposed a model that predicts the sale and purchase curves which set the market clearing price for the day-ahead auction instead of predicting the prices directly. This thesis aims to asses and improve the perfomance of the proposed method in comparison to standard approaches in terms point and probabilistic predictions.
Student: Joao Lima
Supervisor: Mario Beykirch
Time period: 02/04/2019 - 08/04/2019
Type: Master Thesis
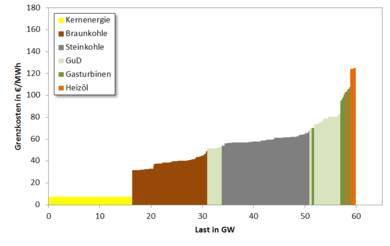
This project aims at understanding in detail how prices at the day-ahead power markets arise, given the technical behavior of all relevant participants is known. This in an important ingredient for modeling future power systems and thus optimizing the course of the Energiewende. Since 2016 the operational schedules of all large power plants in Europe are published on an hourly basis. Given their cost structure and a description of the demand and the renewable infeed it should then be possible to explain the observed power market prices. A straight-forward approach to this problem, however, does not yield satisfying results, an important factor being that it is not clear how to distribute long-term cost components onto individual hours. The project will test and develop different models how to derive the true market prices given the real operation and fixed cost parameters for each power plant.